Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Nishiuchi, Mamiko
Hoshasen Kagaku (Internet), (97), p.13 - 27, 2014/00
Since the first observation of the energetic protons from the interaction between the short pulse high intensity laser and the thin-foil target, extensive studies have been carried out for more than 15 years. In the early period, the laser energy of kilo joule level is necessary to accelerate the protons more than 50 MeV. Such a large amount of laser energy is supplied only by a huge laser system, which typically is unable to make repetitive operation. However, thanks to the progresses in the laser technology, protons having the energies almost 50 MeV are successfully accelerated by the laser system with only less than 10 J of energy and with the capability of repetitive operation. These facts really show the advance of the laser-driven ion acceleration towards the possible fields of applications. Here in this paper the characteristics, the mechanisms and the recent experimental results of the laser-driven proton acceleration are shown.
Esirkepov, T. Z.; Borghesi, M.*; Bulanov, S. V.; Mourou, G.*; Tajima, Toshiki
Physical Review Letters, 92(17), p.175003_1 - 175003_4, 2004/04
Times Cited Count:902 Percentile:99.77(Physics, Multidisciplinary)An intense laser-plasma interaction regime of the generation of high density ultra-short relativistic ion beam is suggested. When the radiation pressure is dominant, the laser energy is transformed effciently into the energy of fast ions.
Matsukado, Koji*; Esirkepov, T. Z.; Kinoshita, Kenichi*; Daido, Hiroyuki; Utsumi, Takayuki*; Li, Z.*; Fukumi, Atsushi*; Hayashi, Yukio; Orimo, Satoshi; Nishiuchi, Mamiko; et al.
Physical Review Letters, 91(21), p.215001_1 - 215001_4, 2003/11
Times Cited Count:136 Percentile:95.24(Physics, Multidisciplinary)no abstracts in English
Daido, Hiroyuki
Reza Kenkyu, 31(11), p.696 - 697, 2003/11
no abstracts in English
Daido, Hiroyuki
Reza Kenkyu, 31(11), p.698 - 706, 2003/11
no abstracts in English
Zhidkov, A. J.*; Koga, J. K.; Sasaki, Akira; Uesaka, Mitsuru*
Physical Review Letters, 88(18), p.185002_1 - 185002_4, 2002/05
Times Cited Count:181 Percentile:96.42(Physics, Multidisciplinary)A strong effect of radiation damping on the interaction of an ultra-intense laser pulse with an overdense plasma slab is found and studied via a relativistic particle-in-cell simulation including ionization. Hot electrons generated by the irradiation of a laser pulse with a radiance of 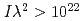 W
W m
m /cm
/cm and duration of 20 fs can convert more than 35% of the laser energy to radiation. This incoherent X-ray emission lasts for only the pulse duration and can be intense. The radiation efficiency is shown to increase nonlinearly with laser intensity. Similar to cyclotron radiation, the radiation damping may restrain the maximal energy of relativistic electrons in ultra-intense-laser-produced plasmas.
and duration of 20 fs can convert more than 35% of the laser energy to radiation. This incoherent X-ray emission lasts for only the pulse duration and can be intense. The radiation efficiency is shown to increase nonlinearly with laser intensity. Similar to cyclotron radiation, the radiation damping may restrain the maximal energy of relativistic electrons in ultra-intense-laser-produced plasmas.
Nishiuchi, Mamiko; Sakaki, Hironao; Pirozhkov, A. S.; Sagisaka, Akito; Kon, Akira; Fukuda, Yuji; Kiriyama, Hiromitsu; Dover, N.*; Sekiguchi, Kentaro; Ogura, Koichi; et al.
no journal, ,
Petawatt class laser systems are in nowadays almost ready to work in all over the world. High energy particles accelerated by the interaction between laser pulses from high intensity laser system and the material shows interesting and particular parameters. Therefore those attract many fields of applications. High contrast and ultra high intensity laser system J-KAREN at KPSI is now under upgrading for achieving highest energy ion beams. No laser system with pulse duration less than 100 fs has demonstrated 100 MeV class proton acceleration in the world. To achieve high energy ions requires higher intensity laser on the target. We report on this presentation the status of the upgrading and the experimental results obtained at the first light experiment.